Themed collection 2024 ChemSci Pick of the Week Collection

Opportunities and challenges for plastic depolymerization by biomimetic catalysis
This perspective highlights the challenges and opportunities in achieving sustainable plastic recycling under mild conditions by imitating the active sites and the substrate-binding clefts of enzymes.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 6200-6217
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC00070F
Revisiting poly(vinyl chloride) reactivity in the context of chemical recycling
An overview of PVC functionalization through the lens of chemical recycling.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 5802-5813
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC06758K
Hybrid and composite materials of organic crystals
Combining organic crystals and polymers results in a new class of all-organic, lightweight, flexible materials with unprecedented mechanical robustness, resilience, and diversity in combination with other functional materials.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 2684-2696
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC06469G
β-Terrecyclene synthase constructs the quadrane backbone in terrecyclic acid biosynthesis
The construction of a quadrane scaffold by β-terrecyclene synthase via Coates' route is demonstrated through mutagenesis and isotopically sensitive branching studies. Subsequent enzymatic modifications convert β-terrecyclene into terrecyclic acid.

Chem. Sci., 2024, Advance Article
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC01208A
A high-resolution structural characterization and physicochemical study of how a peptoid binds to an oncoprotein MDM2
How a peptoid binds to a protein was revealed by a co-crystal structure and systematic physicochemical studies.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 7051-7060
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC01540A
Thermoswitchable catalysis to inhibit and promote plastic flow in vitrimers
We show that weaker acid catalysis has profound effects on the dynamicity of vinylogous urethane based polymer networks. Moreover, the dynamicity could be adjusted by changing electronic and steric parameters in the catalytic environment.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 7061-7071
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC00417E
Ultrafast photogeneration of a metal–organic nitrene from 1,1′-diazidoferrocene
A bent azide intermediate is key to form 1-azido-1′-nitrenoferrocene from 1,1′-diazidoferrocene, as shown with UV-pump–mid-IR-probe transient absorption spectroscopy and density functional theoryTD-DFT calculations including spin–orbit coupling.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 6707-6715
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC00883A
High-throughput single-cell mass spectrometry enables metabolic network analysis by resolving phospholipid C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C isomers
C isomers
A high-throughput single-cell MS platform that can perform both lipid profiling and unsaturated lipid C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C location isomer resolution analysis was developed, which can be effectively used for in-depth structural lipid metabolism network analysis.
C location isomer resolution analysis was developed, which can be effectively used for in-depth structural lipid metabolism network analysis.
![Graphical abstract: High-throughput single-cell mass spectrometry enables metabolic network analysis by resolving phospholipid C [[double bond, length as m-dash]] C isomers](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D3SC06573A&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2024)
Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 6314-6320
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC06573A
Streamlining the automated discovery of porous organic cages
Efficiently merging low-cost high-throughput screening and characterisation, automated data analysis, computational modelling, and cagey – a custom database analysis tool, enhances large-scale data curation and accelerates discovery of organic cages.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 6331-6348
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC06133G
Electronic isomerism in a heterometallic nickel–iron–sulfur cluster models substrate binding and cyanide inhibition of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase
A protein-based model of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase displays distinct X-ray absorption, EPR, and vibrational signatures upon CO and CN− binding that support ligand-dependent electronic rearrangement throughout the nickel–iron–sulfur core.
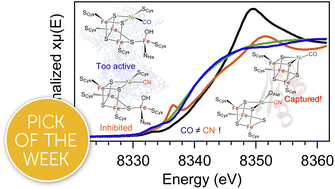
Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 5916-5928
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC00023D
Oxidation-induced ambiphilicity triggers N–N bond formation and dinitrogen release in octahedral terminal molybdenum(V) nitrido complexes
N–N bond formation in octahedral, terminal d1 Mo(V) nitridos to give μ-dinitrogen complexes requires one eletron oxidation with 0.5 equivalents of oxidant to open a kinetically feasible ambiphilic nitrido coupling pathway.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 5152-5162
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC00090K
Delocalisation enables efficient charge generation in organic photovoltaics, even with little to no energetic offset
Simulations reveal that both charge and exciton delocalisation can significantly improve the efficiency of charge generation in organic photovoltaics and explain the failure of classical hopping approaches.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 4779-4789
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC05409H
A covalent organic framework as a dual-active-center cathode for a high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery
We designed a covalent organic framework (TA-PTO-COF) as a dual-active-center cathode. This work presents a promising organic cathode material for a high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 4341-4348
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC07013A
Photoswitchable imines: aryliminopyrazoles quantitatively convert to long-lived Z-isomers with visible light
Simple structural modifications significantly boost the photochromic performance of imine-based photoswitches. This work lays a foundation for exploring new motifs in light-addressable dynamic combinatorial chemistry.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 3872-3878
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC05841G
Iron(IV) alkyl complexes: electronic structure contributions to Fe–C bond homolysis and migration reactions that form N–C bonds from N2
Silylation of iron-alkyl-dinitrogen complexes gives high-spin iron(IV) products that also have an iron(II) resonance structure. The stability and reactivity of these compounds depends on the alkyl group, with insertion and homolysis observed.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 3485-3494
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC05939A
Busting the myth of spontaneous formation of H2O2 at the air–water interface: contributions of the liquid–solid interface and dissolved oxygen exposed
The air–water interface is not the site for H2O2(aq) formation; instead, it takes place at the solid–water interface.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 3093-3103
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC06534K
PoseBusters: AI-based docking methods fail to generate physically valid poses or generalise to novel sequences
PoseBusters assesses molecular poses using steric and energetic criteria. We find that classical protein-ligand docking tools currently still outperform deep learning-based methods.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 3130-3139
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04185A
A scalable synthesis of adjuvanting antigen depots based on metal–organic frameworks
ZIF-8 vaccine enhances the humoral immune response through sustained antigen exposure to the immune system whilst zinc adjuvants the vaccine via inducing T cell activation.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 2731-2744
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC06734C
Alternatives to fluorinated binders: recyclable copolyester/carbonate electrolytes for high-capacity solid composite cathodes
A series of poly(ester-b-carbonate) electrolytes are prepared by a one-pot procedure and structure–property relationships are observed. The polymer was used as a composite cathode binder with excellent discharge capacity and capacity retention.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 2371-2379
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC05105F
Designing solvent systems using self-evolving solubility databases and graph neural networks
Our self-evolving graph neural networks for predicting solubilities reconciled different magnitudes of errors and uncertainties of experimental and computational databases, maximizing the database size and the model’s prediction accuracy.

Chem. Sci., 2024,15, 923-939
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03468B
About this collection
In 2018, the Chemical Science Editorial Team launched ‘ChemSci Pick of the Week’ as a means to select and promote our favourite articles from the week and share them with the wider chemical community. This on-going web collection showcases all ChemSci Picks from 2024, which are highlighted on our journal social media pages via the #ChemSciPicks hashtag.